
With 2025 already off to a rocky start thanks to governments everywhere falling apart, a psychotic buffoon elected President of the U.S.A., intractable wars in Africa, Europe, and the Middle East, and the everlooming threat of climate change hanging over the world, there's never been a better time to consider the merits of stoicism. The problems of the world are too overwhelming and unsolvable so, rather than sink into despair, stoicism offers up a different way of looking at things and managing our emotions.

Take warfare for example. For over 2,000 years Europe has been at war with itself in a seemingly endless clash of ideology and religion to establish the boundaries of nations and empires in one form or another. From Greek and Roman empires through to the Middle Ages and then World Wars 1 and 2 it has never let up and here we are at it again with the Ukraine and Russia. Since it doesn't seem likely this will ever end or that the Europeans will ever learn from history why should we worry about it? Even before the Europeans, the various empires of the Middle East have been conquering one another over the ages with the Babylonians, Egyptians, Persians, Ottomans, and ultimately the Europeans trying to take control of the region with predictable results. Once again add a little ideology and religion into the mix and you have perfect conditions for endless warfare.

Global warming is another example of something we may have to examine in a different way. There's no denying we have put more CO2 into the atmosphere as a result of our fossil fuel consumption but unfortunately this is only going to get worse because our energy consumption is growing faster than we can supply it rather than slowing down. Even as we add solar, wind, and nuclear energy we still need the fossil fuels and other energy sources to maintain all of our activities. Energy intensive facilities such as new data centres to power AI and other technologies, are only adding to the problem. As energy historian Jean-Baptiste Fressoz points out in his book,
More and More and More: An All-Consuming History of Energy, evolving high-energy societies incorporate their old energy addictions into new ones to solve more problems and, as a result, consume more energy of any kind. Rather than transitioning from consuming wood to coal, for example, we end up using even more wood to build timbers in coal mines and for building railways to haul the coal. Likewise we use even more coal to manufacture steel and other products to enable us to extract oil and transport it by pipeline.
Guera Mountains in southern Chad
There is however a positive aspect to all this increased CO2 in the atmosphere and that is the planet is starting to get greener. From the semi-arid Sahel region, a 3,900 km area stretching east-west across Africa south of the Sahara desert, to the deserts of northern China and southeast Australia, the world's drylands are turning green and the reason is surprisingly simple. Plants grow by photosynthesis (sunlight, water, CO2) and the high concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere makes it easier for this to occur and lets the plants use less water in the process. According to a Yale University study, validated by the University of California, there has been a 12% increase in photosynthesis world wide since 1982 as a result of this CO2 fertilization. So, while the Earth is indeed warming, the threat of desertification is receding and plants are moderating the build-up of gas in the atmosphere.
Alpine National Park in Victoria, Australia
Until we use up all the fossil fuels on Earth we will continue burning them and, as we continue to electrify the grid, our energy consumption will also increase as we mine more and more rare minerals to build the cars, solar panels, windmills, data centers, and nuclear power plants that will follow. We already know the end result of a warming planet is more rapidly melting polar caps, flooding, hurricanes, and forest fires but, because we can't prevent these things from happening, we instead need to learn how to live with these events and build our cities accordingly.

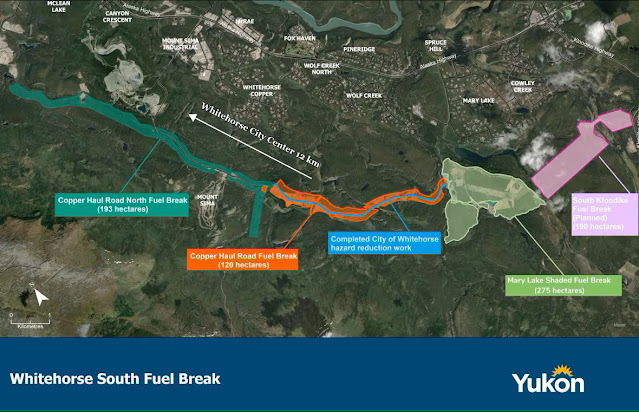
For example in Whitehorse, Yukon a 20 kilometre long fuel break around the south end of the city is being built to help prevent a wildfire from entering. The width of the break is between a few hundred metres to two kilometres. By removing coniferous trees and shrubs from the landscape and replacing them with slower-burning deciduous trees like aspen, the city will have a "living infrastructure" to help with firefighting efforts. Keeping buildings away from flood plains is another obvious preventative measure cities could encourage.
In the end the world's problems may not ever be solvable but there may be steps that can be taken to mitigate how they affect us. Focusing on happiness rather than despair will take some of the stress out of our lives. By practising a little Stoicism we may learn to simply let it be.



.png)
















.webp)















